What is the Cause of Psoriasis?
The cause of psoriasis is unknown to doctors. They do, however, have a rough concept of two critical elements, genetics and the immune system, thanks to decades of research.
Immune system
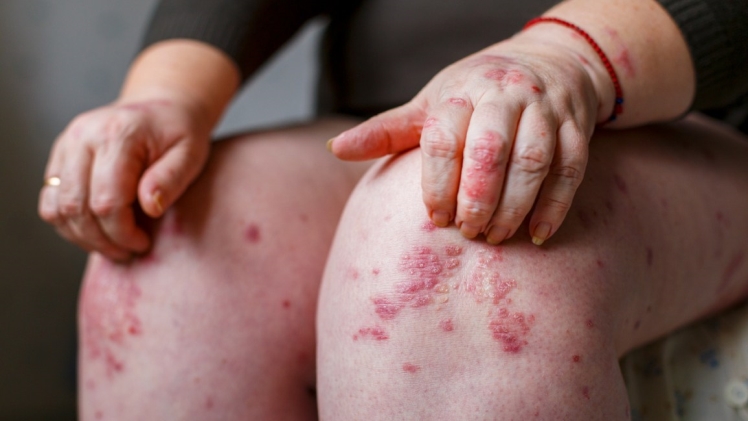
Psoriasis is a type of autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases develop when the body attacks itself. T cells, which are white blood cells, wrongly target skin cells in psoriasis.
White blood cells are used to attack and eliminate invading bacteria and combat infections in the human body. The skin cell development process goes into overdrive as a result of this erroneous onslaught. New skin cells develop too quickly as a result of the accelerated skin cell production. They’re forced to the surface of the skin, where they build up.
Visit The Site: bestmagzine90
The plaques that are most typically associated with psoriasis are the outcome of this process. As a result of the attacks on skin cells, red, inflammatory regions of skin appear.
Genetics
Some people are born with genes that make them more susceptible to psoriasis. You are more likely to develop psoriasis if you have a close relative who has the skin condition. However, the number of persons with psoriasis with a genetic susceptibility is in the minority. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, about 2 to 3% of people with the gene get psoriasis (NPF).
Psoriasis Diagnosis
Psoriasis may require two tests or examinations to be diagnosed.
Examination of the body
A simple physical exam is enough for most clinicians to make a diagnosis. Psoriasis symptoms are usually obvious and distinguishable from those of other illnesses that can generate similar symptoms.
Make careful to show your doctor any areas of concern during this exam. Also, tell your doctor if any members of your family have the disease.
Biopsy
A small sample of skin may be taken if the symptoms are unclear or if your doctor wants to confirm their initial diagnosis. A biopsy is the medical term for this procedure.
The skin will be transported to a lab and inspected under a microscope. The test can determine which type of psoriasis you have. It can also be used to rule out other illnesses or infections.
The majority of biopsies are performed on the day of your appointment in your doctor’s office. To make the biopsy less unpleasant, your doctor will most likely inject a local anesthetic. The biopsy will then be sent to a lab for analysis.
When the results come back, your doctor may schedule an appointment with you to go over the findings and treatment choices.
Psoriasis Treatment Options
Psoriasis has no known cure. Treatment, on the other hand, can make you feel better. It’s possible that you’ll need topical, oral, or systemic medications. There are effective strategies to manage psoriasis flare-ups even if you have severe psoriasis. You might be able to fully eliminate your symptoms.
- Topical treatments: These are medications that you apply straight to your skin. They’re usually the first thing your doctor would recommend, along with a decent moisturizer, especially if you have mild to moderate psoriasis. Prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications are available. Topical psoriasis treatments include ointments, creams, and foams, and include:
- Salicylic acid: Scaly skin can be softened and thinned with this treatment. However, if you keep it on for too long, it can irritate your skin. It may also weaken your hair follicles, resulting in temporary hair loss. If you apply salicylic acid to broad areas of skin, it might be absorbed by the body.
- Calcipotriol: This is a high-potency synthetic vitamin D supplement. It has been shown to regulate hyperactive skin cells. It may be used with steroid cream by your doctor.
- Tazorac (Tazarotene): is a gel or cream that should be used once or twice a day. It is not advised for women who are pregnant, nursing, or planning to get pregnant.
- Immunosuppressants: These aren’t steroids, but they do alter the function of your immune cells. Pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are two options. These may be prescribed by your doctor for use on sensitive areas such as your face, groin, or skin folds.
- Retinol with a prescription: These are vitamin A ointments that have been synthesized. Your doctor may also recommend that you take a steroid at the same time. This may reduce the likelihood of retinoid-induced skin irritation.Read More About: bestweb345